What is NAD+, and why you should take it?
What Is NAD⁺ and What Is the Best Way to Supplement It ?
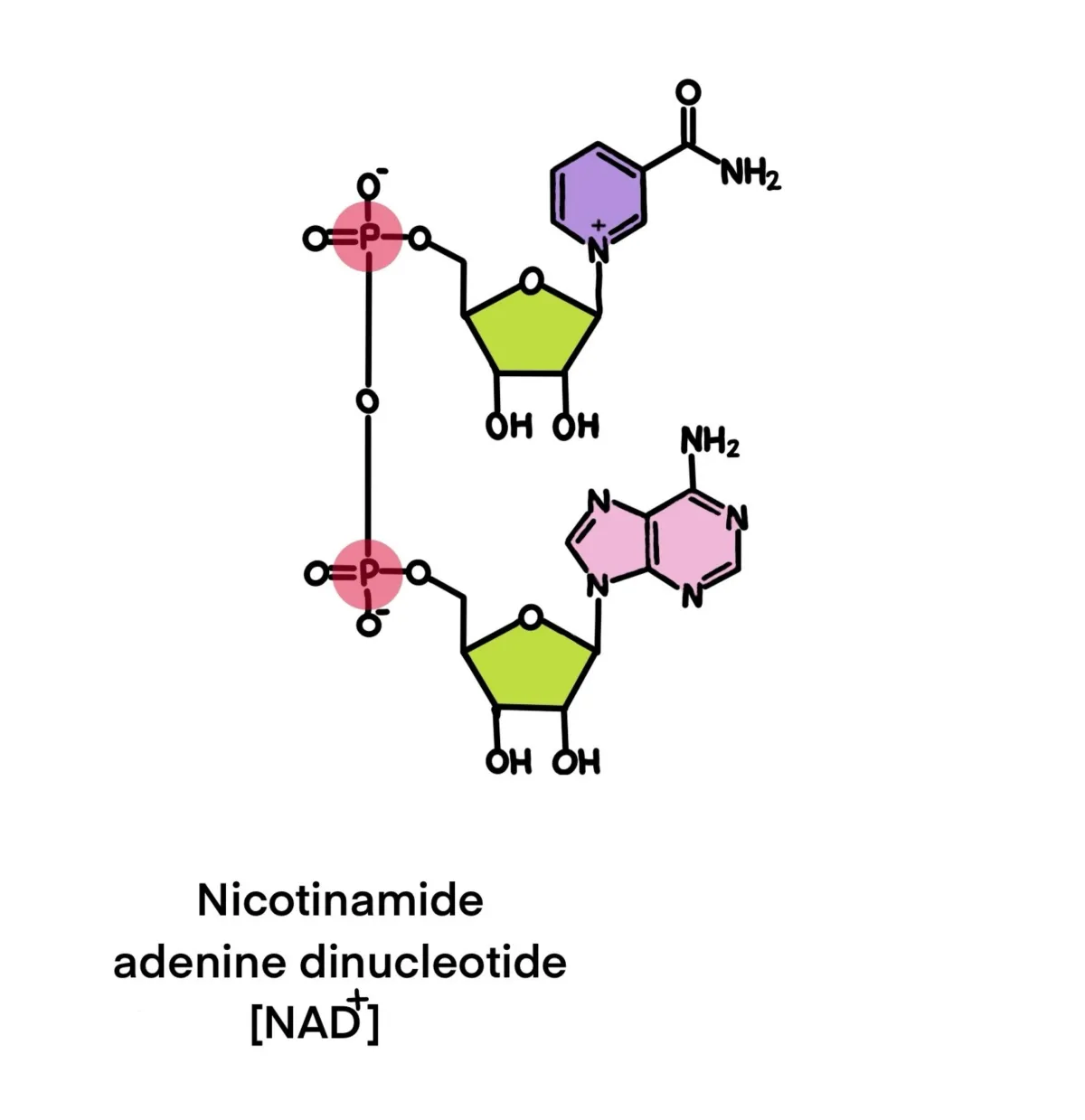
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD⁺) is an essential coenzyme found in every living cell. It participates in over 300 cellular reactions and plays a central role in:
Energy production (ATP synthesis)
DNA repair and cellular regeneration
Mitochondrial function
Sirtuin activation (anti-aging pathways)
Redox reactions and antioxidant defense
NAD⁺ functions as a key electron carrier during oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. Without sufficient NAD⁺, cells cannot efficiently convert nutrients into ATP—the body’s primary “energy currency.”
Why NAD⁺ Declines With Age
NAD⁺ levels naturally decrease by 40–60% between ages 40 and 60 due to:
Increased inflammation (activating CD38, a major NAD-consuming enzyme)
Oxidative stress
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Greater demand for DNA repair
Decreased endogenous synthesis
This decline is strongly associated with metabolic dysfunction, fatigue, decreased cognitive performance, and accelerated aging.
Potential Health Benefits of Optimizing NAD⁺
Research—both human and translational—suggests that maintaining optimal NAD⁺ levels may support:
1. Brain & Cognitive Health
Enhances neuronal energy metabolism
Slows age-related cognitive decline
Supports neuroprotection (via SIRT1 and SIRT3)
Key evidence: NR increased NAD⁺ in the brain and improved cognitive markers in older adults (Brady et al., 2022).
2. Chronic Fatigue & Mitochondrial Support
Higher NAD⁺ availability improves mitochondrial ATP production and may reduce fatigue seen in:
Chronic fatigue states
Long COVID
Age-related energy decline
Key evidence: IV NAD⁺ increased energy and mitochondrial function markers in small clinical trials.
3. Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health
NAD⁺ precursors show benefits for:
Insulin sensitivity
Fat oxidation
Lowering triglycerides
Improving endothelial function
Key evidence: NR improved lipid parameters and reduced inflammatory cytokines (Martens et al., 2018).
4. Anti-Aging & Cellular Repair
NAD⁺ activates sirtuins, PARPs, and other longevity-associated enzymes:
DNA repair
Reduced oxidative damage
Improved autophagy and mitophagy
Maintenance of telomere integrity
5. Inflammation & Immune Modulation
Acts as a cofactor for enzymes involved in cellular defense and immune regulation.
Key evidence: NAD⁺ repletion showed anti-inflammatory effects in human macrophages and in vivo models.
Clinical Uses of NAD⁺ in Functional & Regenerative Medicine
Common NAD⁺-related clinical applications include:
Anti-aging protocols
Chronic fatigue and mitochondrial dysfunction
Cognitive decline / neuroprotection
Metabolic optimization (insulin resistance, obesity)
Alcohol or drug detox support (under physician supervision)
Adjunct therapy for neurodegenerative conditions (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s—experimental)
Age-X Clinics often use a combined strategy: IV NAD⁺ for rapid restoration + oral precursors for maintenance.
What Is the Best Way to Supplement NAD⁺?
There is no single “best” option—each has specific benefits. The most studied NAD⁺ precursors are:
1. NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
Pros:
Direct precursor to NAD⁺
Strong evidence in metabolic health and cellular aging
Good oral bioavailability
Rapid conversion into NAD⁺
Evidence:
NMN improved muscle insulin sensitivity in postmenopausal women (Yoshino et al., 2021).
Best for: anti-aging, metabolic support, mitochondrial health
2. NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)
Pros:
FDA-recognized as GRAS
Well-studied in humans
Improves NAD⁺ in blood and tissues
Potential cognitive benefits
Limitations: conversion to NMN required before reaching NAD⁺.
Evidence:
NR improved blood pressure and arterial health in older adults (Martens et al., 2018).
3. NAD⁺ IV Therapy
Pros:
Immediate elevation of systemic NAD⁺
Can achieve higher levels than oral supplements
Useful in clinical settings: fatigue, detox, neuro support
Limitations:
Must be administered by trained clinicians
Time-intensive (60–180 minutes)
Best for: patients seeking rapid NAD⁺ restoration.
4. Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Effective but limited by flushing and GI side effects.
So Which Is the Best? (Clinically)
For longevity and metabolic optimization, most practitioners—including many in regenerative medicine—prefer:
→ Daily NMN or NR (for long-term maintenance)
→ Periodic IV NAD⁺ (for rapid elevation or therapeutic use)
Age-X Protocol Example:
IV NAD⁺ 250–500 mg monthly or as needed
NMN 300–500 mg/day (or NR 300–600 mg/day) for maintenance
Combine with sirtuin-activating lifestyle factors: exercise, fasting, red/infrared light therapy
At Age-X clinics we will help you to restores your NAD+levels and boost your energy and metabolism to increase your lifespan and most importantly your healspan, call us at
813-751-3570 for the Apollo Beach office
940-303-4120 for the Bradenton office,
References (Clinically Relevant & High-Quality)
Martens CR et al. Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD⁺ in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Nat Comm. 2018.
Yoshino M et al. NMN increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science. 2021.
Brady NN et al. Nicotinamide riboside increases brain NAD⁺ and improves neurodegeneration biomarkers. Aging Cell. 2022.
Rajman L, Chwalek K, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic potential of NAD⁺ boosting strategies in aging and disease. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 2018.
Verdin E. NAD⁺ in aging, metabolism, and neurodegeneration. Science. 2015.
Poddar SK et al. NAD⁺ and mitochondria: implications in aging and disease. Cell Metabolism.
CD38 and NAD depletion research: Chini CC et al. Trends Mol Med. 2018.